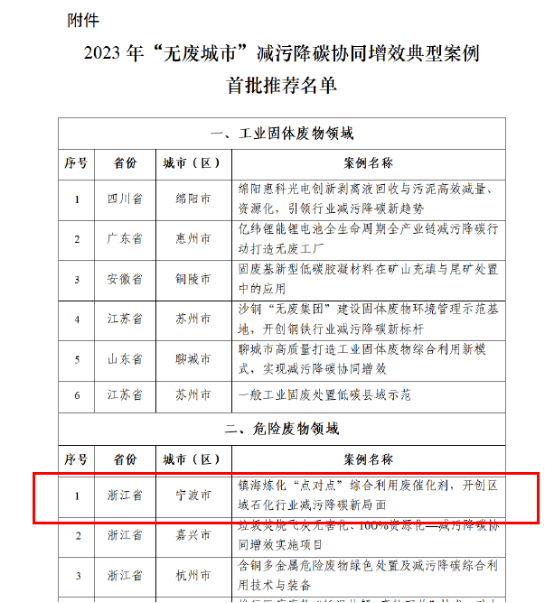
Typical cases of Ningbo Zhenhai's "point-to-point" project listed as "waste-free cities"
Recently, the Asia-Pacific Regional Center for the Basel Convention announced the first batch of 36 typical cases of synergy in pollution reduction and carbon reduction in "waste-free cities" in 2023. The list of "Zhenhai Refining and Chemical Industry" submitted by Zhenhai District of Ningbo City is on the list of "Point-to-Point" Comprehensive Utilization of Waste Catalysts to Create a New Situation of Pollution Reduction and Carbon Reduction in the Regional Petrochemical Industry "was listed.
The Basel Convention Regional Center for the Asia-Pacific is authorized by the Secretariat of the Basel Convention and under the dual leadership of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment and Tsinghua University. It is one of the 14 Basel Convention regional and coordinating centers in the world and the only authorized center of the Basel Convention Secretariat in China.
In August last year, the center launched a collaborative effort to reduce pollution and reduce carbon emissions in "waste-free cities" based on the "2023" Waste-Free Cities "Construction Work Promotion Plan"(Huanban Jishi Han [2023] No. 99) document of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment, and received a total of 176 cases submitted by various places. After material form review, expert preliminary and final evaluation, 36 first batch of recommended cases for pollution reduction and carbon reduction in the construction of "waste-free cities" were produced. The "point-to-point" project of China Petrochemical Zhenhai Refining and Chemical Company was selected as the only case in Ningbo City.

Zhenhai Refining & Chemical "point-to-point" directional utilization device
The second phase refining project of Sinopec Zhenhai Base led by Zhenhai Refining and Chemical Co., Ltd. has built a 6 million tons/year deep catalytic cracking (RTC) unit. According to the process characteristics, it requires equilibrium catalysts to start up; while CNOOC Ningbo Daxie Petrochemical Co., Ltd. The 2.2 million tons/year catalytic cracking (DCC) unit produces about 150 tons of catalytic cracking balance agent (spent catalyst) per month, which belongs to HW50 hazardous waste. After investigation and analysis, the performance indicators of Daxie Petrochemical spent catalyst meet the start-up requirements of the new RTC unit in the second phase of Zhenhai Base.
Under the guidance of the local ecological environment department, Zhenhai Refining and Chemical completed the preparation and review of the "point-to-point" project plan last year in accordance with the "Implementation Plan for the Pilot Work of Exemption Management of" Point-to-Point "Directed Utilization Business License of Hazardous Waste in Zhejiang Province", and was approved by Ningbo in March. The Municipal Ecological Environment Bureau approved it and began to accept spent catalysts from the Daxie Petrochemical DCC unit, becoming the city's first "point-to-point" targeted utilization case of hazardous waste.
According to preliminary estimates, after the implementation of the "point-to-point" project, it can reduce hazardous waste disposal by about 3000 tons and reduce total carbon dioxide emissions by about 10050 tons.

Sinopec Zhenhai Base under Construction
Next, Zhenhai District will deeply explore the green waste-free production model of the petrochemical industry, promote the construction of a "1+24 waste-free petrochemical base" with Zhenhai Refining and Chemical as the core, focus on upstream and downstream related units in the industrial chain, and comprehensively tap the potential of corporate waste reduction. Zhenhai Refining and Chemical Co., Ltd. is the first "Waste-Free Group" pilot unit in Zhejiang Province to obtain approval from the Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Its "shared hazardous waste utilization and disposal facilities within the group" model has greatly reduced the outsourcing disposal of hazardous waste, with a reduction ratio of 40%; The company has also jointly promoted a new model of self-disposal and utilization of hazardous waste such as concentration reduction, incineration disposal and terminal treatment, and is expected to reduce the production of waste alkali liquor by more than 200,000 tons every year.







