What impact will the dimming of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau have?| Interview with the second Qinghai-Tibet scientific expedition team

China Environment News: The results of the top ten landmark results of the second Qinghai-Tibet scientific expedition show that Asian water towers are dimming. How can researchers use scientific research to predict and evaluate the impact of surface dimming on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau on climate?
Tang Shuchang:During the second Qinghai-Tibet expedition, we evaluated the changes in the surface albedo on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on multi-source observation data. These observations include observation records from field stations and observations based on various satellite remote sensing. These multi-source observation data show that the surface albedo of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau has indeed gradually decreased in recent years, and the average results of multiple models CMIP5 and CMIP6 also show that the downward trend of surface albedo of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau will continue with a high probability in the future. This means that the proportion of reflected radiation from the surface of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau decreases, and more radiation is absorbed by the surface. If you look at the ground from space, the surface will darken.
At present, observations and models are mainly used to assess the impact of surface dimming on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau on the climate system. First, with the help of the Earth system model, a virtual "digital earth" is built. Through extremely complex computer code sets, activities in various layers of the Earth system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, biosphere, etc., as well as various layers. Complex interactions between layers. Subsequently, the surface albedo data obtained from satellite remote sensing observations and the surface albedo data superimposed on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau with the predicted future albedo decline were input into the Earth system model to form two comparative experiments. The difference between these two experimental results can be regarded as the impact of the decline in the surface albedo of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, which is the impact of "surface dimming of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau."
With the help of combining observations and models, under the joint guidance of Academician Park Shilong, captain of the Second Qinghai-Tibet Expedition Team, researcher Wang Tao of the Institute of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and researcher Li Xichen of the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, we discovered that the impact of surface darkening on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is not only limited to the plateau and its surrounding areas, but also radiates to more distant polar regions and even affects the global climate system.
China Environment News: What are the specific impacts of surface dimming on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau on polar climate change and global climate?
Tang Shuchang:The research results found that the future surface dimming of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau will profoundly affect the polar climate and the global climate system. For the Arctic climate, the future surface dimming of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau will lead to warming of the Arctic North Atlantic Ocean and its surrounding areas near Greenland, and cooling of the high-latitude areas of Eurasia next to it. This dipole pattern of "polar North Atlantic warming-Eurasian high-latitude cooling" exists in all seasons and is strongest in winter.
In winter, the dimming of the plateau surface will lead to a significant increase in the temperature of the polar North Atlantic by about 0.55 degrees Celsius, accounting for 9.4% of the increase in near-surface temperature in the region at the end of this century; while the temperature in the high latitudes of Eurasia will significantly decrease by about 1.61 degrees Celsius, which is-19.9% of the future change in near-surface temperature in the region. This result shows that the long-range climate effect of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau on the polar regions cannot be ignored.
Subsequently, based on this set of experiments, a new round of experiments was conducted to assess the impact of changes in Arctic sea temperature and sea ice. The research results show that the future increase in sea temperature and the melting of sea ice in the Arctic will heat the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau through atmospheric processes. These two sets of experiments revealed that there is a complex interaction between the surface darkening of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and climate change in the Arctic. That is, the surface darkening of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau heats the Arctic; the changes in the Arctic sea temperature and sea ice will in turn heat the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, causing the plateau vegetation to turn green and glacier snow recede, which will lead to further darkening of the plateau surface. This is one of the important developments in the second Qinghai-Tibet expedition.
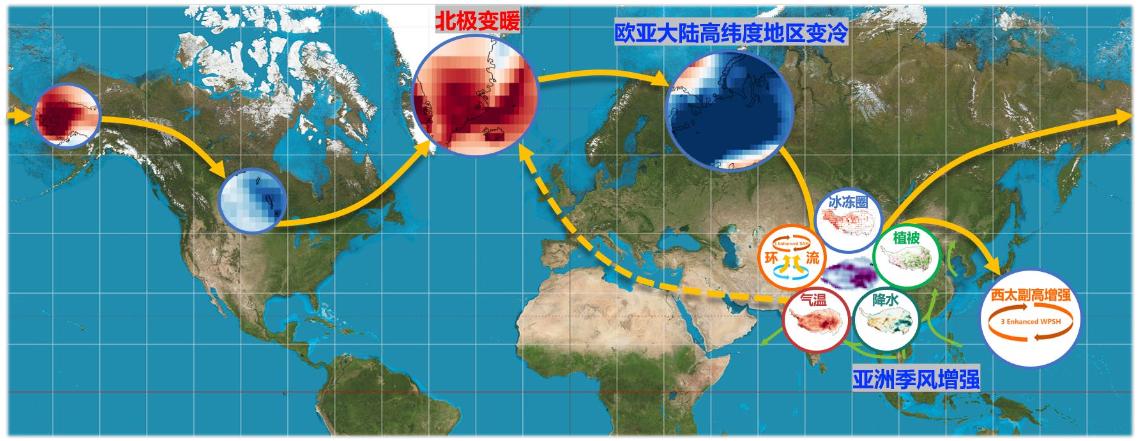
Impact and feedback of surface dimming on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau on the region, surrounding areas and mid-to-high latitude climate systems in the northern hemisphere.
In addition to the Arctic climate system, the research results also found that surface dimming on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau has an important impact on the global climate system. For example, the future surface dimming of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau will lead to regional warming, while regional precipitation will show a dipole change pattern of "increasing in the east and decreasing in the west", resulting in significant degradation of regional glaciers, especially those in the western part of the plateau, in the future. In addition, the future surface dimming of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau will affect the Asian summer monsoon by regulating the South Asian high and the Western Pacific subtropical high, resulting in enhanced summer monsoon precipitation in South Asia, while the phenomenon of "floods in the south and drought in the north" in East Asia will intensify in summer. Of course, the global climate system does not only include the above-mentioned regions. We are also conducting follow-up research and analysis to assess the climate effects of surface dimming on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau on other regions, and hope to gain a deeper understanding of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau's impact on the global climate system. important impact.

China Environment News: What are the specific impacts of surface darkness on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau on the local ecosystem? How should we protect fragile ecosystems?
Tang Shuchang:The impact of surface darkening on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is not limited to the climate field, but will also have an impact on the local ecosystem. However, it should be emphasized that the dimming of the plateau surface itself stems from the enhancement of local vegetation growth and greenening. The impact of plateau surface dimming on the ecosystem we are talking about here refers to the improvement of plateau vegetation, resulting in surface dimming. In the background, the degree of impact of plateau surface dimming on the ecosystem in turn, that is, the feedback of plateau surface dimming on the ecosystem. The results of the second Qinghai-Tibet scientific expedition show that in the future, the local leaf area index will increase slightly and the total primary productivity will also increase under the surface darkening scenario of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, which will eventually increase the plateau land carbon reserves by about 0.81 PgC, accounting for the current plateau land carbon reserves. 1.5% of the carbon reserves.
Overall, surface dimming on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau will benefit the local ecosystem. However, from a spatial perspective, due to the decrease in precipitation and warming effects that aggravate the lack of soil water, the surface darkening of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is not conducive to vegetation growth in the arid areas of southwestern Tibet. Faced with this challenge, response measures need to be prepared in advance to protect local fragile ecosystems. For example, laws and regulations related to ecological protection on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau can be further established and improved, and the number of local livestock can be reasonably controlled without affecting the lives of local herders to achieve a balance between grass and livestock; a monitoring network can also be built on the plateau to warn the plateau will face Extreme climatic events and natural disasters; and a number of new water conservancy facilities can be built to replenish enough water to the drought-affected ecosystems of the plateau by regulating runoff.
China Environment News: How to slow down the trend of surface darkening on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau through scientific methods?
Tang Shuchang:To alleviate the trend of surface darkening on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, we need to first know why the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau has darkened. The research results show that the reduction of glacier snow cover, the enhancement of vegetation growth, changes in soil moisture, rapid urbanization, and changes in aerosol concentration will all affect the albedo of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Among these influencing factors, some are favorable, such as improving plateau vegetation. There are also some that can be alleviated through scientific methods. For example, black carbon aerosols are the product of incomplete combustion of fossil fuels and biomass fuels. They have strong light absorption and are also an important factor in the dimming of the plateau surface. Carbon aerosols from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau are mainly imported from external sources. Therefore, we can work with neighboring countries to jointly reduce black carbon emissions and control black carbon concentration to protect the stability of the "Asian Water Tower" and mitigate the trend of darkening.
In addition, by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, achieving the "double carbon" goal as soon as possible, and working with other countries in the world to curb the current trend of global warming and reduce the melting of highly reflective glacier snow on the plateau, it can also alleviate the situation of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. The trend of surface darkening.
China Environment News: In recent years, extreme weather events have occurred frequently, which are inextricably related to global warming and surface dimming on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. How should we scientifically understand this phenomenon and take effective measures to alleviate this phenomenon?
Tang Shuchang:At present, many studies have shown that the current increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme climate events such as global heat waves and floods is related to global warming, especially the "warming amplification effect" of the "three poles", namely the Antarctic, Arctic, and Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. degree of correlation. The changes in surface processes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau are also inextricably related to the frequency and intensity of extreme events in surrounding areas and even Eurasia. According to some research data, surface dimming on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is associated with extreme events. We are conducting corresponding research, hoping to clarify the connection between the two as soon as possible, and provide a new perspective for understanding the mechanism of extreme events and the important role of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in the Earth system.
As for mitigation measures, they can be divided into two parts. One is to curb the increasing trend in the frequency and intensity of extreme events, and the other is to enhance human ability to adapt to extreme events. First of all, we must reduce greenhouse gas emissions, achieve the "double carbon" goal as soon as possible, and use international negotiations and other measures to work with other countries in the world to curb or even reverse the current trend of global warming, thereby reducing the frequency and intensity of extreme events at the source. Secondly, it is necessary to improve the whole society's awareness of the frequent occurrence of extreme weather and its serious hazards, and further improve and optimize the current emergency management system. For example, a sound climate change monitoring and risk assessment system should be established as soon as possible, and dynamic and real-time monitoring should be implemented with the help of advanced monitoring instruments, such as radar, satellite remote sensing, etc. In addition, public publicity and early warning mechanisms for extreme events should also be improved. When extreme events occur, early warnings should be disseminated in an all-round way through the use of television, radio, Internet, text messages, etc. to increase the public's response time to extreme events and improve the public's response. Ability to extreme events reduces loss of life and property.







